Future of CRM with SAP S/4HANA
Category: SAP S/4HANA Posted:Jul 10, 2018 By: Robert
SAP has been working on the integration of a basic version of SAP CRM into S/4. On the basis of S/4 release in September 2017, the original product roadmap provided the first customer release of an integrated product in the early months of 2018. The actual integration was scheduled as an add-on to S/4. The previous scope of this particular CRM add-on for S/4 was intended to cover what is known as Core Service functionality. The year 2019 has been earmarked for yet another release which will cover additional sales and service functionality which will include migration and loyalty management tools. Statements about the strategic differences between CRM section of S/4 and SAP Hybris CRM and CEM systems have not been clear and product roadmaps have also been suffering from lack of clarity.
Learn SAP S/4HANA Simple Finance from Industry Experts
SAP, S/4HANA and the CRM Plans
It has become evident now that the anticipated release will be delayed by a considerable amount of time along with changes in the original plans of release. A webinar organized for each partner, SAP had announced two intriguing modifications with the one change being related to the other. SAP CRM will cease to be called as an add-on to S/4, instead, it will be known as SAP S/4HANA for Customer Management. This will be true, at least for the service functionality. Considering this, the service part of SAP CRM followed by the sales portion will become a part of S/4. CRM marketing will also be phased out and SAP Hybris marketing will be phased into its place.
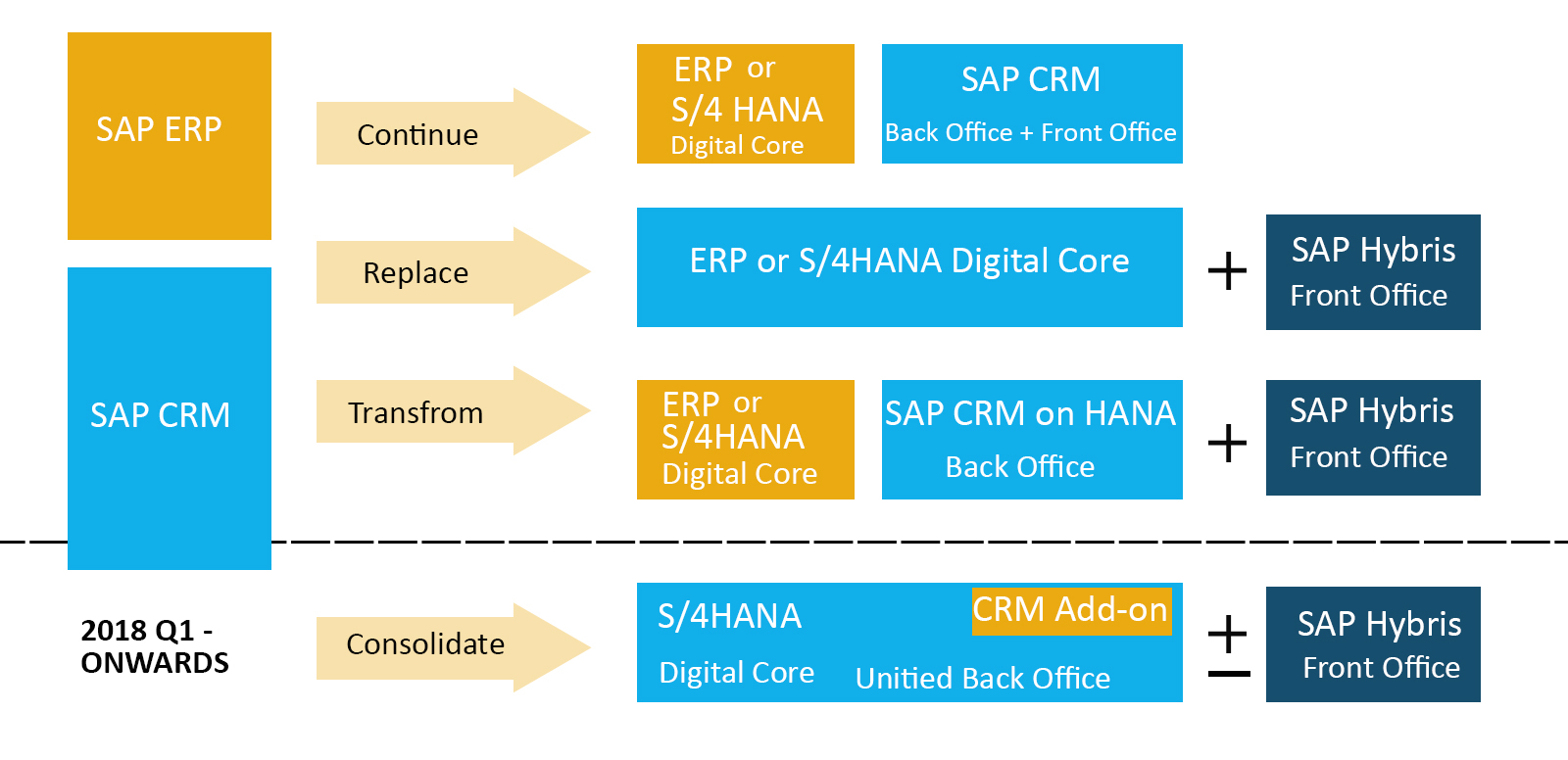
There are various difficulties and challenges when combining two complex and distinct sections of software into a reliable product. Even though SAP would have anticipated the challenges, currently it looks like they are higher than was originally thought. Therefore, merging software instead of providing said software’s in terms of add-ons has increased the complexity involved in delivering greatly. The ‘Sales Core’ that will follow the Service Core is still planned for 2018.
Service Simplification
Since S/4 is light on customer service functionality SAP’s release sequence makes sense. This can also be viewed in business object models which make up the joint solutions and their sources. Adding the CRM interaction Centre is also a smart choice, even though this will have other consequences when dealing with the SAP Hybris engagement center.
SAP has chosen to utilize transactional objects from CRM and to merge them with an S/4 variation of Master type of objects. The primary exception here includes the business partner which will have its origins in CRM. As the CRM business partner is considerably enhanced than the original ERP business partner this exception is logical. This is getting the best of both worlds.
Sales Simplification
Such a theme will continue in the sales domain, where ERP based S/4 functionality is more robust than in the service section. Another argument in favor of this is that order fulfillment is a core ERP task. In any case, there will be no need for having two distinct object models in the very same system. Two intriguing features here are an option of CRM based organizational model and the inclusion of a loyalty element into S/4. Loyalty management is a classic component in the software product.
The majority of other CRM engines and frameworks, such as reporting, extensibility, pricing, and configuration, etc. will be substituted by their corresponding S/4 / ERP counterparts or be converted into a part of external engines. Overall, the CRM for S/4 picture is rounded off.
But there are various queries that SAP has to answer to earn the customer/stakeholder confidence. Some, such queries include:
- How well defined and detailed is the distinction between S/4 for Customer Management and the diverse SAP Hybris solutions?
- How trustworthy is the roadmap? This is a forever challenging question. But the discreet shift of the release of S/4 for Customer Management from being based on 1709 to H2, 2018 can bring up some further queries. Conversely, the timeline for delivery is not yet acute, because there is continuing support for CRM till the year 2025.
- How do you deal with numerous ERP or S/4 backend systems? There are already a considerable number of clients that run different ERP systems in different countries or for different subsidiaries solely for legal and associated reasons. The first plan for a CRM add-on did not cover this common situation. There still is no statement about it other than CRM Middleware still being part of the system.
- How do you deal with engines and industry solutions? The most conspicuous example, currently is CPQ and the forthcoming SAP Revenue Cloud.
S/4 Customer Service vs. SAP Hybris
The final question is a major one with the answer to the same emerging gradually. There are three system tiers that include systems of engagement, systems of operation, and Systems of record. The bulk of the transactional load is taken up by the system of record. The system of engagement and the Cloud- based operational system provide nimbleness and flexibility needed by quickly changing consumer engagement needs. Hence the transaction system is based on S/4 whereas the engagement and operation systems are founded upon the SAP Cloud platform. This means that everything can be placed within the Cloud and the transactional system has and can stay on-premise.
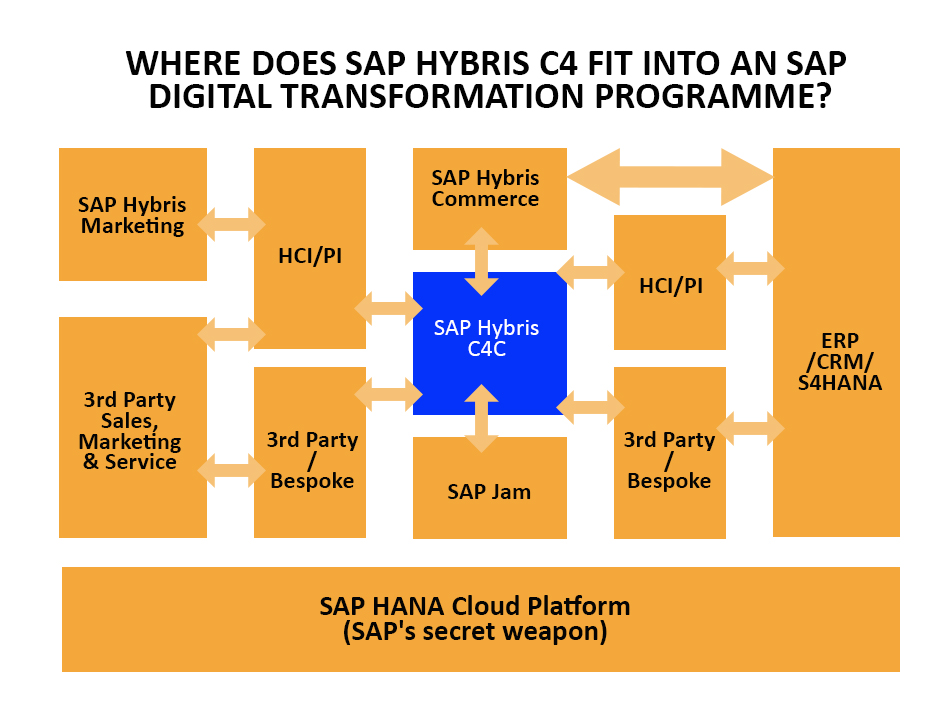
A Customer Service Example
When considering customer service and SAP implementation on a conceptual level of its vision, it is easy to conclude that SAP’s focus has always been on customer service. The segmentation of systems into three layers is not necessarily needed. This is because Field Service and Omni-channel service engagement both have customer engagement and operational aspects.
Three-tiered framework for SAP & SAP Hybris Customer Service
Differentiating the Framework as mentioned above makes sense. But one has to pay attention to the details, as they suggest inaccurately, that the system of engagement is actually on top of the operating system – Hence merging low volume high-touch service and high volume Low touch service. This opens up the suggestion to the fact that service tickets need a Cloud for implementation of service along with Omni-channel customer engagement center. But this is completely inaccurate.
For instance, the two systems provide service tickets even though the service ticket in Cloud for customer needs provides more functionality. Instead of this, the Cloud for services is focused on being a Field Service Management solution which is market-leading and includes better mobile experience and advanced scheduling capabilities. And in the case of the engagement Centre, it will focus on agent-based and automated customer service with both solutions being supported by SAP Leonardo-based machine learning.
And the problem here is- SAP provides service ticket intelligence solutions to classify incoming service tickets automatically and to offer suggestions for resolution for the Agents. This enables contact centers to speed up the resolution of problems and also scale with the Spikes in digital service requests. This will mean accelerated resolution of tickets through ticket routing to the right agents and also, by offering solution suggestions, reducing the resolution times. On top of this, it frees up the agents to spend more time with customers instead of doing admin or system management tasks. The consolidated effect of this should be enhanced customer service and improved customer satisfaction as clear business outcomes. But SAP service ticket intelligence will come integrated into the SAP service Cloud. And this is the apparent reason for the different number of tickets needed for the learning process.
But conversely; executing the ticket intelligence against the Cloud for the consumer with the agents working within the service engagement center or S/4 based interaction center – The ticket intelligence will not connect to the system which serves for ticket creation and will therefore not really help agents. This does not work effectively with self-service systems and is at best inconsistent. It may force SAP customers to implement a superfluous and unneeded system.
The complete picture is gaining more clarity with each passing day and the distinction between the old transaction systems and the current systems of engagement is becoming more apparent. Looking at the progress that SAP is making, CRM will become a part of ERP S/4 and CEM will become the brand-new customer engagement and Commerce which is driven by SAP Hybris. Current queries about SAP products are about how to integrate the Cloud platform products such as SAP Leonardo and distinct SAP Hybris solutions optimally to arrive at a consistent and customized customer solution. The existing problem for consumers with this is the overlap in terms of functionality of different Clouds which are merged with modularization that is insufficient.
Here the rework of YaaS can be considered. Making the Clouds both modular and turning those into micro services would enable seamless recombination of systems. This also allows the definition of functional scope as per customer needs as against providing pre-packaged systems. In order to provide additional support for customers, one can visit the integration strategy for various elements with the objective of reducing the number of systems required. One issue that may crop up during implementation is SAP Hybris versus SAP which should not occur. Both sections of enterprise need to work in conjunction to provide solutions customers need. Inter departmental competition might affect customer service and cause service issues and should be avoided.
SAP CRM into S/4HANA
SAP has always speculated on the future of SAP CRM – if there will be a CRM element in S/4HANA. A highly placed representative of SAP has stated that SAP is currently working on adding CRM functional for HANA and also merging SAP CRM into it. Also Desirable is combining SAP Hybris C4C into S/4HANA. This approach would lead to a cleaner code base.
The prime benefits of merging SAP CRM into S/4HANA over SAP Hybris C4C are:
1. It will open a future roadmap for current SAP CRM customers that stretch beyond 2025. Otherwise, such customers would obviously opt for other products in its place.
2. This will offer the sustainable option for customers to run their SAP instance on-premise. According to SAP representatives, there are still a lot of customers that do not want to run their instance in the Cloud. The key term here is customer choice.
3. This will simplify the system landscape and its operation as well.
And this method will work, despite SAP seemingly having various research efforts that explain in detail that SAP CRM could never work as part of an ERP system.
The Current Scenario
The SAP is merging SAP CRM into S/4HANA and it will not be a simple and easy to merge and will turn into an add-on for S/4HANA. This is an intriguing move in itself as in this manner it will not be possible to continue using preexisting SAP CRM as a standalone feature. There are also a few consumers who are using SAP CRM without ERP integration. A few customers might not even own an SAP ERP and the others still would be limiting themselves by not moving on to S/4HANA from SAP ERP.
2017 for Service Functionality
The product roadmap says that SAP will begin with delivery of service functionalities as a component of the CRM add-on. This makes sense because S/4HANA is currently missing out on customer service. This particular functionality will have an RTC founded upon the S/4HANA 1709 release. S/4HANA will also stand to gain from a stronger business partner had by SAP CRM, as contrasted with the current S/4HANA and ERP as well. This mainly depends on S/4HANA master data objects. The scope of such interlinked functionality is open and the core service functionality mainly focuses on shared services and utility industries. This is because there will not be massive migration tools with the first release.
2018 for Sales Functionality
SAP has earmarked the year 2018 for the delivery of core sales functionality with the robust use of S/4HANA objects, excluding the flexible organizational model brought in by CRM. CRM will also add a good number of CRM associated objects which S/4HANA is missing such as loyalty, territory, opportunities, and leads. S/4HANA core will also work on delivering billing, pricing, configuration and order, along with the development, and delivery of migration tools.
Marketing for 2019
The short version answer to this question is no. of Post the release of sales core, 2019 will witness a focus on rounding off the service and service functionality with the inclusion of loyalty and management. SAP also has an SAP Hybris Marketing which has a marketing solution which can be implemented on demand and on-premise as well.
SAP and CRM
The SAP is considering individual business objects and also deciding on which particular object to use and the manner in which it is to be used. To avoid expensive redundancies and CRM Middleware objects will get harmonized, with the Middleware stays untouched.
Particularly the highly normalized one-order model will get de-normalized. This will utilize the pre-existing index tables that got introduced to get some performance into the CRM Order model. This will also support the HANA Database which highly prefers wide tables over to joins.
User Interface
SAP S/4HANA makes use of a Fiori User Interface. But one can make the CRM Web User Interface resemble a Fiori User Interface. This gives additional support through the delivery of Fiori apps for overview pages along with chosen native Fiori apps. Also, this is augmented by the Fiori Launch Pad integration. This is similar to the existing User Interface in SAP Hybris Marketing.
Register Now for Live webinar on SAP S/4HANA Simple Finance
Conclusion
It is definitely a good strategy to merge SAP CRM into SAP S/4HANA. Some customers will probably like a broader footprint right from the start, but the object sequence for this merge makes great sense. That’s also very little pressure for SAP to migrate immediately to SAP continuing to support through the year 2025 and it is a great concept to continue gaining from stability. Customer-driven innovation strategy will have to wait until migration tools are functioning.
Enterprises looking to move to S/4HANA are required to finish above-mentioned migration first. Synchronizing all data models will also mean that a migration from SAP CRM to S/4 CRM will be treated as a migration project and will require a stable S/4HANA as a pre-requirement. What might prove to be a concern would be the positioning of S/4 CRM against SAP Hybris Cloud solutions which might create an “us vs. them” situation. The considerable overlap in functionality in might dent customer service. SAP has a lot of work to do for indicating when a solution needs to be worked on to avoid any confusion. All being said and done, SAP is bound to continue its legacy of excellence through its CRM integrations and will retain its customers in the process.





 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999