What is Quality Assurance in Project Management?
Category: Quality Assurance Posted:May 15, 2017 By: Serena Josh
Quality
There has been extensive research on this subject and a lot has been written about quality by many quality experts. The most significant and widely accepted definition of quality is given by Mr. Philip B. Crosby which states “Quality is Conformance to requirements”.
According to ISO 8402:1996, i.e. Quality Management and Quality Assurance Vocabulary standard states that Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or a service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.
According to ISO 9000:2000, i.e. the set of International Quality Standards and Guidelines for Quality Management Systems states that Quality is the degree to which a set of existing characteristics fulfil requirements.
Simply put, you can say that “quality is about meeting the customers’ requirements” and the deliverable being fit for use. When a product meets or exceeds customers’ requirements and needs one can say that the product is of high quality. Conversely, if it is not meeting its stated requirements the product is said to be of low quality.
Quality Assurance
Quality simply means fitness to use and conformance to requirements. Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on the processes utilized in the project efficiently to generate quality project deliverables. It includes the following meeting standards, progressive enhancing project work and eliminating project defects.
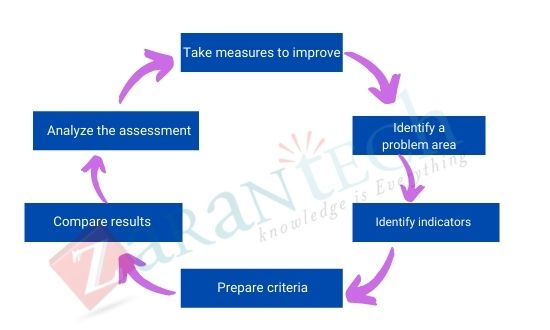
Quality Assurance assures the quality of the product meaning that this process ensures that the product generated from the process is defect free and conforms to all stated customer requirements. It is said to be a process-based approach whose primary objective is to prevent defects in deliverables at the planning stage to avoid rework, which increases process costs.
Quality Assurance can also be viewed upon as a proactive process and it places importance on planning, documentation, and guidelines finalization that will be needed to assure the quality. This process begins at the very start of the project to compare the product’s requirements and expectations. Once all requirements and expectations are recognised, a plan is developed to meet these requirements and expectations.
Tools used in the Quality Assurance Process
There are fundamentally three tools utilized in quality management – process analysis, quality audit, and quality management and control tools. In process analysis, one analyses the process to spot any enhancements, find the root cause of any problem that comes up, and recognize any non-value added activities.
In , Quality Audit, a panel of external experts come and review the process and procedures. If they discover any discrepancies, they will recommend corrective action or an enhancement in the process. It is an excellent tool to ensure the best practice and approved procedures are being followed.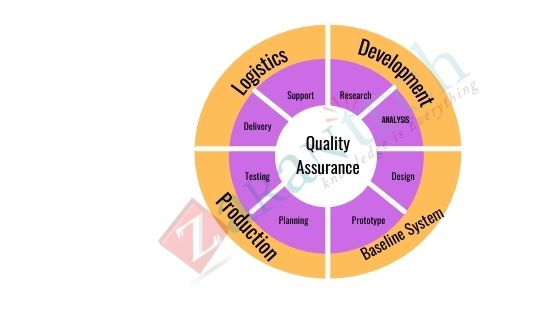
Quality management and control tools include different diagrammatic techniques which aid in discovering ideas, help make decisions, and prioritize issues.
Learn Quality Assurance from Industry Experts
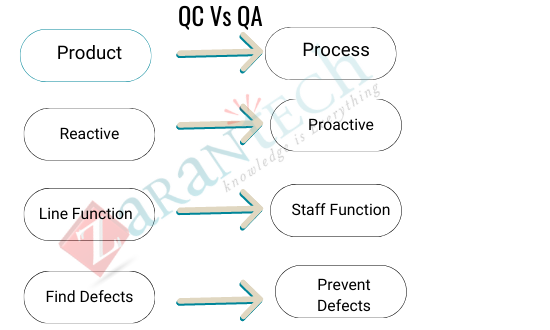
The Difference between Quality Assurance and Quality Control:
- Quality Assurance stresses on defect prevention and Quality Control focuses on defect identification.
- In quality Assurance, one checks if the plan was efficient enough to avoid any forecasted defect. In Quality Control, one attempts to find defects and correct them while creating the product.
- Quality Assurance is a proactive process whereas Quality control is a reactive process.
- Quality Assurance is a process-based approach whereas Quality Control is a product-based approach.
- Quality Assurance includes processes managing quality, and Quality Control is utilized to validate the product quality.
- Quality Audit is an example of Quality Assurance. Inspection and testing are great examples of the Quality Control process.
The Benefits of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
The following are few benefits of these processes:
- High quality output
- Eliminate waste or in the very least minimize waste
- Increase the efficiency of operations by a large factor
- Offer customer satisfaction, which positively affects your brand and helps individuals and organizations grow their business
- Less rework and after-sale support is needed. This will aid one save a lot of money
- Promote high levels of confidence and a motivated team
Quality Assurance and Quality Control are closely interlinked and their objective is also the same, which is to deliver a defect-free product.
Both processes are key components of a quality management plan and augment each other. Failing to implement either of them will lead to failure of quality management in the project.
Quality Assurance is one of the prime features in the Project Management space and one of the most rapidly transforming areas in software creation.
Quality Assurance Activities: Planning, Auditing and Analysing Project Quality
Quality Assurance activities are those tasks the quality team executes to view the quality requirements, audit the results of control measurements and analyse quality performance in order to make sure that right quality standards and procedures are appropriately applied within the project.
The Quality Assurance Activities is an article of the Quality Management Section in the Project Implementation Guide. It explains the three kinds of activities to aid the Project Manager and the quality team to formulate a quality assurance plan template, audit quality performance and review project activities, procedures and processes.
Given below are the three key activities of Quality Assurance:
Develop a Quality Assurance Plan
The first of the Quality Assurance activities includes planning the overall process for assuring quality. Its purpose is to formulate a Quality Assurance plan template which is a highly efficient tool to assure quality in a project and surveil problems and drawbacks that may come up during the project execution process. The quality team is required to utilize such a plan to do the rest of the Quality Assurance activities, such as Audit and Analysis.
The fundamental steps in creating a Quality Assurance plan template are sequential and start off with setting up goals of project assurance as to why the project would need Quality Assurance. The next step would be to designate responsibilities to members of the quality team and decide the hierarchy of management such as who will carry out the Quality Assurance activities. Collect the relevant project standard information and define compliance criteria such as how to make Quality Assurance. Recognize a set of measurements and metrics to be utilized to gauge quality levels and performance which involves checking whether the project is performed under appropriate quality levels.
Register for Quality Assurance Live Webinar
Audit Project Quality
A quality Audit is a standard, systematic review of project activities to recognize whether these activities are executed in line with business processes and tactical decisions. The goal of executing a project quality audit is to show the missing or inefficient policies, procedures and/or processes that decreases quality levels and increases the probability of project failure. During a supervised conventional quality audit session under Project Manager can review quality metrics such as defect frequency, budget deviation, failure rate, on-time performance, and gauge project activities against the quality baseline.
Auditing quality permits recognition and correction of any deficiencies in project activities. As a process it leads to minimize cost of quality management and highly improved product acceptance and customer satisfaction. Frequently, quality auditing activities are executed by the external and independent auditors who offer expert knowledge and advice.
The Quality Assurance activity generates a formal confirmation document that proves required changes to the execution process and acts as a foundation for formulating corrective actions.
You may also like to read : What is Quality Assurance?
Analyze Project Quality
Quality Analysis is a group of steps to inspect and investigate a particular project activity and recognizes what would improve the activity’s value. The objective of project quality analysis is to review quality levels and define required enhancements in the current quality management framework.
The Quality Assurance activity permits examination of problems encountered, deviations in constraints, and any tasks and processes that provide value. It involves fit analysis, root cause analysis, techniques for recognizing and resolving issues, and techniques for formulating corrective actions. For example, during fit analysis, product testing is utilized as a method for scrutinizing product features and checking that they match the user acceptance criteria. A testing plan will transform into a scenario for analysing, assuring and verifying product quality.
Review Project Activities
Once the Quality Audit and Analyses are executed the next step would be to introduce the recommended changes in project processes through project process review. This will complete the Quality Assurance process cycle.
Project Quality Assurance Techniques
The Project Manager for developing a new product or service will be in a position to influence quality. If the Project Manager is a participant in the design phase of the project, the manager can largely affect the choice of design specification and their alternatives. The Project Manager will oversee the testing and evaluation phase of the development project. The Project Manager is expected to direct and offer inputs to the design of the quality control system that will check ongoing production. In short, the Project Manager is in a prime position to influence and assure a quality project.
With respect to the quality outcome of a project, the Project Manager should have the following among his objectives:
- The design of the product, service, or construction meets the customer’s requirements and specifications within targeted market segment.
- This design is reasonably close to an optimum configuration, offering maximum value in terms of function and cost, considering the utilization of materials, reliability, design configurations, serviceability and in some cases, aesthetic appeal and more.
- The product is completely safe and does not have unwanted side effects, and is significantly secure from misuses.
- The product will be competitive that offers a good value when it reaches the market.
- The process by which the product is manufactured is well understood so that the process can be optimized, controlled, and rapidly restored to equilibrium in case of disturbances.
- The product will perform as intended in a reliable manner with negligible downtime and lengthened life.
While the above pointers pertaining to the outcome of the project, another part of the equation is the need to execute the whole project as rapidly and inexpensively as possible.
The Project Quality Assurance techniques that will help make it happen are as follows:
Cause/Effect Matrix
It is the ideal time to begin a potential problem analysis while the project is still in the design phase. The Cause/Effect matrix is a great way to execute this analysis. Simply put, this method in an exhaustive checklist of possible pitfalls. But instead of a simplistic list, the causes and effects be arranged in a two dimensional array with all the system or product attributes, components, or performance components listed in one dimension; all the possible disturbing causes listed in another.
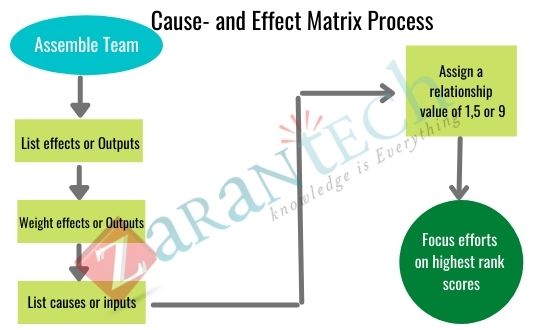
In each cell there is space for an indication of the probability of each cause having a negative effect on the system function. These probabilities which range from 0 to 1.0, has to be supplied by knowledgeable design, production, Quality Control, Sales Engineers, and, if possible, by a sample of customers. They would indicate the probability that a certain cause in the path of production or product use would have an observable adverse effect on the system function. All high probabilities, most likely, are intolerable, and the condition generating the high probability should be set right.
Learn Quality Assurance from Industry Experts
Brainstorming
This is largely a random flow of uninhibited ideas by a team. This technique is sometimes useful for uncovering novel solutions to non-technical problems. It may be useful for somewhat technical problems if an attempt is made to classify responses in a manner that will lead to other ideas.
The functional analysis diagram is a useful technique to classify the brainstorming output. The diagram is built by a verb-noun objective statement to the left with a verb-noun tree of supporting concepts emerging to the right. Simply put, the “WHY‘S” are to the left; the “HOW‘S” are to the right.
Synectics
This is another approach to creativity that uses analogies. Conventionally, a team of engineers attempting to enhance a design are asked to formulate analogies from another branch of science to view how an identical problem was solved. A mechanical problem, for instance, might have a counterpart in the animal or plant world. Theoretically, the study of the structure of bird calls can be used to solve a data transmission problem.
Process Mapping
The controllable variables that influence a process like temperature, voltage, quantity of materials etc. probably can be comprehended and characterized if there are only two to four critical variables, and they are independent. However, if there is an interaction between the controllable variables and uncontrollable variables then the issue turns more complex and becomes subject to failure.
Mapping is the activity through which a process is purposefully subjected to variations in the control variables in order to characterize the process. There are three reasons for doing this work:
- Process can be modelled and optimized.
- Sensitivity can be gauged
- Better comprehension how to correct the process if it is disturbed by uncontrollable or unknown variables.
Conclusion
Quality Assurance processes are meant to make a product defect-free and make sure it conforms to requirements. Quality Assurance is a process-based approach. Quality Assurance architects a process so that the product coming from this process is defect free.These processes have critical roles in the project success. Their effectiveness can only be actualized completely when they are well understood by the enterprise and the team executing the job.
I hope that by now you have had an overview of Quality Assurance in Project Management. Before you enroll in ZaranTech’s certification course on QA, do check out the tutorial for Beginners:




 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999